A Mesh network uses multiple devices, called nodes, to expand Wi-Fi coverage throughout your home or office. It distributes the Wi-Fi signal across several nodes, ensuring strong connectivity even in hard-to-reach areas.
Understanding and Setting Up a Mesh Network
How does a Mesh Network work?
A mesh network operates by using a primary central router, often called the main node, along with several satellite routers, or nodes, that connect wirelessly to the main router. These satellite nodes work together to create a unified and expansive Wi-Fi network. Here's how it works:
-
Central Router: The main router is connected to your internet source (like a modem) and serves as the primary hub for the network.
-
Satellite Nodes: These additional nodes are placed throughout the area you want to cover. They wirelessly connect to the main router and to each other, forming a web-like structure.
-
Seamless Connectivity: As you move around, your device automatically connects to the nearest node with the strongest signal, ensuring a stable and fast connection without interruptions.
-
Extended Coverage: By strategically placing satellite nodes, you can eliminate dead zones and ensure strong Wi-Fi coverage in every corner of your home or office, even in areas with obstacles like walls or floors.
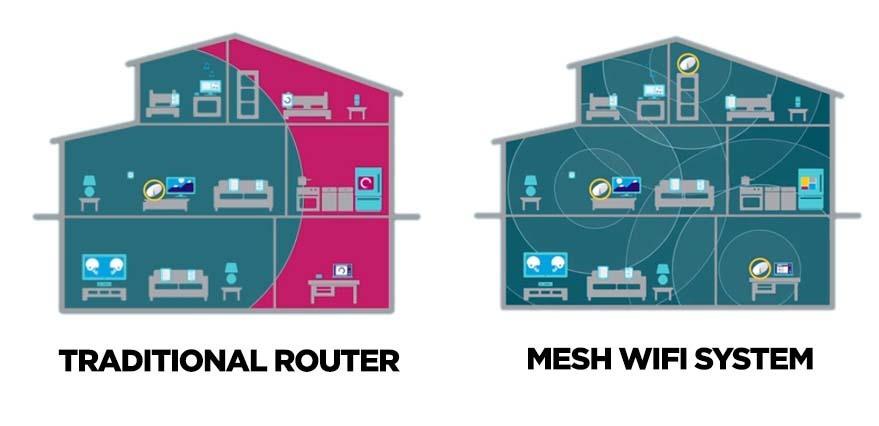 Fig 1: Traditional routers vs Mesh WiFi systems
Fig 1: Traditional routers vs Mesh WiFi systemsIssues Resolved by a Mesh Network
Mesh networks address several common Wi-Fi issues:
- Dead Zones: Traditional routers often struggle to cover large areas, leading to dead zones. Mesh networks eliminate these by using multiple nodes.
- Seamless Roaming: Unlike extenders, which create separate networks, Mesh networks allow devices to switch seamlessly between nodes without dropping the connection.
- Consistent Speed: Extenders can degrade signal strength and speed as you move further from the main router. Mesh networks maintain consistent speeds throughout the coverage area.
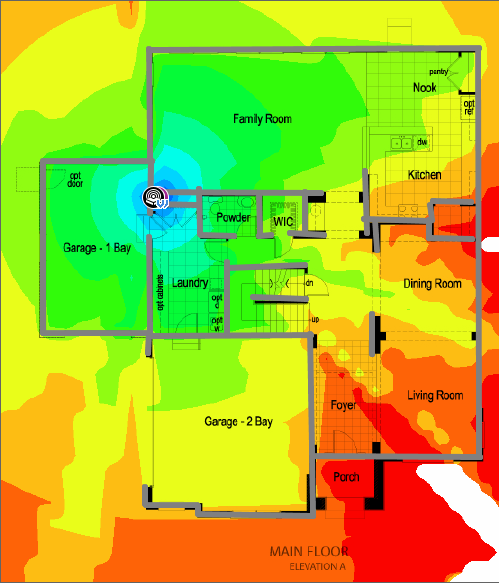
Fig 2: Wi-Fi dead zones
Mesh Networks vs. Wi-Fi Extenders
Mesh Networks:
- Unified Network: All nodes operate under a single network name, providing seamless connectivity.
- Better Performance: Mesh networks offer consistent speeds and better performance across the entire coverage area.
- Easy Management: Managed through a single app, making setup and maintenance straightforward.
Wi-Fi Extenders:
- Separate Networks: Extenders create separate networks, which can cause connectivity issues as devices switch between them.
- Signal Degradation: The further you are from the main router, the weaker the signal and speed.
- Complex Setup: Extenders often require manual configuration and can be more challenging to manage.
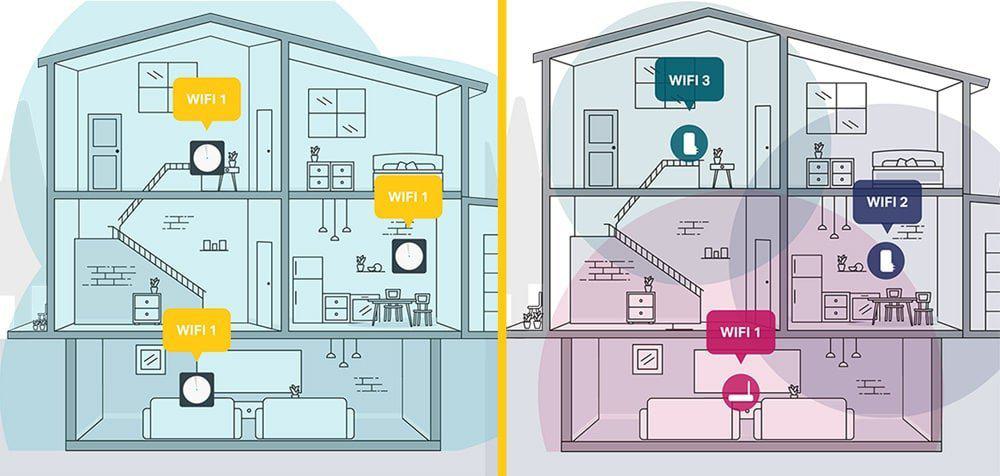
Fig 3: WiFi Extenders vs Mesh WiFi System
Optimal Placement of Mesh Network Nodes
To get the most out of your Mesh network, proper placement of the nodes is crucial:
-
Overlap Coverage:
- Ensure that the coverage areas of the nodes overlap. This helps maintain a strong connection between nodes and prevents dead spots.
- Ensure that the coverage areas of the nodes overlap. This helps maintain a strong connection between nodes and prevents dead spots.
-
Height Matters:
- Place nodes higher up, such as on shelves or bookcases. This helps the signal propagate better throughout your home.
-
Avoid Obstacles:
- Keep nodes away from large metal objects, thick walls, and other obstacles that can interfere with the signal.
-
Central Locations:
- Position nodes in central locations within your home to maximize coverage. Avoid placing them near outside walls.
-
Line of Sight:
- Aim for a clear line of sight between nodes whenever possible. This ensures the best possible signal strength and stability.
- Aim for a clear line of sight between nodes whenever possible. This ensures the best possible signal strength and stability.

By following these placement tips, you can ensure your Mesh network provides robust and reliable Wi-Fi coverage throughout your space. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out to our support team.
